-
 Exec linked to Bangkok building collapse arrested
Exec linked to Bangkok building collapse arrested
-
Zelensky says Russian attacks ongoing despite Putin's Easter truce

-
 Vaibhav Suryavanshi: the 14-year-old whose IPL dream came true
Vaibhav Suryavanshi: the 14-year-old whose IPL dream came true
-
Six drowning deaths as huge waves hit Australian coast

-
 Ukrainian soldiers' lovers kept waiting as war drags on
Ukrainian soldiers' lovers kept waiting as war drags on
-
T'Wolves dominate Lakers, Nuggets edge Clippers as NBA playoffs start

-
 Taxes on super rich and tech giants stall under Trump
Taxes on super rich and tech giants stall under Trump
-
Star Wars series 'Andor' back for final season

-
 Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
-
Tariffs could lift Boeing and Airbus plane prices even higher

-
 Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big MLS crowd in Cleveland

-
 Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
-
'Pandora's box': alarm bells in Indonesia over rising military role

-
 Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
-
Trio share lead at tight LA Championship

-
 Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
-
Recovering pope expected to delight crowds at Easter Sunday mass

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
-
Force skipper clueless about extra-time rules in pulsating Super Rugby draw

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big crowd in Cleveland

-
 Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
-
Another round of anti-Trump protests hits US cities

-
 'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
-
PSG maintain unbeaten Ligue 1 record, Marseille back up to second

-
 US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to block Trump deportations

-
 Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
-
Pacers thump Bucks to open NBA playoffs

-
 Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
-
Zelensky says Ukraine will observe Putin's Easter truce but claims violations

-
 'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
-
DR Congo boat fire toll revised down to 33
-
 England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
-
Verstappen's Red Bull 'comes alive' to claim record pole in Jeddah

-
 McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
-
Rajasthan unleash Suryavanshi, 14, as youngest IPL player but lose thriller

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
-
Villa rout Newcastle to rekindle bid to reach Champions League

-
 Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
-
Trans rights supporters rally in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling

-
 'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
-
Bordeaux-Begles backups edge Pau to close in on Top 14 summit

-
 Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
-
PSG beat Le Havre to stay on course for unbeaten Ligue 1 season

-
 Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
-
14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player

-
 Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
-
Zverev sets up birthday bash with Shelton in Munich


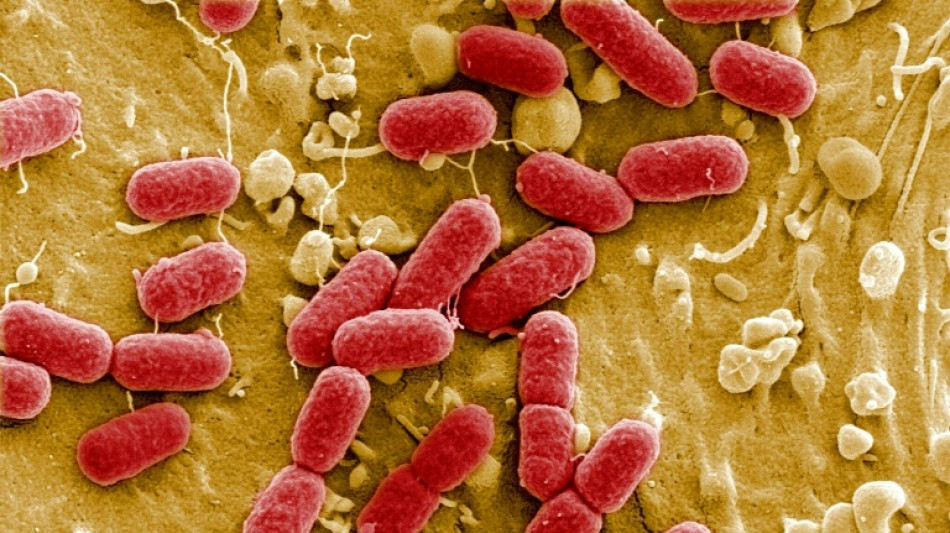
Harmful pollution boosting superbug 'silent pandemic'
Containing and cleaning up environmental pollution, especially in waterways, is crucial to controlling increasingly bullet-proof superbugs which could kill tens of millions by mid-century, a new UN report said Tuesday.
Superbugs -- strains of bacteria resistant to antibiotics -- are estimated to have killed 1.27 million people in 2019, and the World Health Organization says antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the top global health threats on the near-term horizon.
Up to 10 million deaths could occur every year by 2050 because of AMR, the UN says.
The disinfectants, antiseptics and antibiotics that can help microbes become stronger are everywhere, from toothpaste and shampoo to cow's milk and wastewater.
A new report Tuesday said pollution is a key driver in the "development, transmission and spread" of AMR, calling for urgent action to clean up the environment.
"With increasing pollution and lack of management of sources of pollution, combined with AMR in clinical and hospital settings and agriculture, risks are increasing," said the report from the UN Environment Programme.
Antimicrobial resistance is a natural phenomenon, but the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans, animals and plants has made the problem worse.
This means antibiotics may no longer work to fight the very infections they were designed to treat.
The UN report Tuesday said that pollution in the environment from key economic sectors has exacerbated the problem, namely from the pharmaceutical and chemical manufacturing sectors, along with agriculture and health care.
Herbicides to control weeds on farms may also increase AMR, while heavy metals are also contributing to the problem.
Once antimicrobials enter the environment they seep into the food chain -- they've been found in fish and cattle -- and loop back into factories making everyday toiletries, for example.
- 'Silent pandemic' -
Antimicrobial resistant genes are in waterways across the globe, from the Ganges River in India to the Cache la Poudre River in the US state of Colorado, the UN study found.
"This is a real issue, because rivers are often the source of our drinking water," Jonathan Cox, senior lecturer in microbiology at Britain's Aston University, told AFP.
"It's already the silent pandemic," warned Cox, who is not linked to the UN study. "It is becoming the next pandemic without us really recognising it."
Prevention is key, the UN said.
"Fuelled by population growth, urbanisation and growing demand for food and healthcare, we can expect an increase in the use of antimicrobials and in pollutant releases into the environment," it said.
The UN urged governments and international groups to address "key pollution sources", including sewage, city waste, healthcare delivery, pharmaceutical manufacturing and intensive crop sectors.
Cox said solutions need to be global, since AMR is so pervasive.
One answer is to focus on clinical approaches, such as improving rapid testing for infections so that antibiotics are not incorrectly prescribed.
Another is improving wastewater management to remove antimicrobials. But such processes are complicated and costly.
"The technology is out there, it just isn't being employed because governments don't care so much about the environment as they do about the bottom line," Cox said.
K.Thomson--BTB




