
-
 A stadium and a jersey for Argentina's 'Captain' Francis
A stadium and a jersey for Argentina's 'Captain' Francis
-
New Trump task force vows to root out 'anti-Christian bias'

-
 Auto Shanghai showcases new EV era despite tariff speedbumps
Auto Shanghai showcases new EV era despite tariff speedbumps
-
Trump's administration moves to scrap artificial food dyes

-
 Musk to reduce White House role as Tesla profits plunge
Musk to reduce White House role as Tesla profits plunge
-
US official backs off promise to solve cause of autism by September

-
 Guardiola joy as Man City go third after dramatic win over Villa
Guardiola joy as Man City go third after dramatic win over Villa
-
Trump says has 'no intention' of firing Fed chief

-
 Jury finds New York Times did not libel Sarah Palin
Jury finds New York Times did not libel Sarah Palin
-
UN appoints envoy to assess aid for Palestinians

-
 Celtics star Tatum 'doubtful' for game two against Magic
Celtics star Tatum 'doubtful' for game two against Magic
-
Former England star Flintoff reveals mental battle after car crash

-
 Defending champion Korda chases first win of season at Chevron Championship
Defending champion Korda chases first win of season at Chevron Championship
-
Olmo fires Liga leaders Barca past Mallorca

-
 Nunes strikes at the death as Man City sink Villa to boost top-five bid
Nunes strikes at the death as Man City sink Villa to boost top-five bid
-
Tesla says profits plunge 71%, warns of 'changing political sentiment'

-
 WHO announces 'significant' layoffs amid US funding cuts
WHO announces 'significant' layoffs amid US funding cuts
-
PSG draw with Nantes to stay unbeaten in Ligue 1

-
 Trump's administration moves to ban artificial food dyes
Trump's administration moves to ban artificial food dyes
-
Gunmen kill dozens of civilians in Kashmir tourist hotspot

-
 US Treasury chief expects China tariff impasse to de-escalate
US Treasury chief expects China tariff impasse to de-escalate
-
I.Coast opposition leader Thiam barred from presidential election

-
 Top US court leans toward parents in case on LGBTQ books in schools
Top US court leans toward parents in case on LGBTQ books in schools
-
At least 24 killed in Kashmir attack on tourists

-
 Rahul powers Delhi to big win over Lucknow in IPL
Rahul powers Delhi to big win over Lucknow in IPL
-
Colombian cycling star 'Lucho' Herrera denies murder conspiracy

-
 Trump, Zelensky to attend Pope Francis's funeral Saturday
Trump, Zelensky to attend Pope Francis's funeral Saturday
-
US State Department to cut positions, rights offices

-
 Ukraine ready for direct talks with Russia only after ceasefire: Zelensky
Ukraine ready for direct talks with Russia only after ceasefire: Zelensky
-
Myanmar Catholics mourn pope who remembered their plight

-
 Pope's Vatican 'family' pay tearful respects
Pope's Vatican 'family' pay tearful respects
-
The world leaders set to attend Pope Francis's funeral

-
 'Like a storm': Witnesses describe deadly Kashmir attack
'Like a storm': Witnesses describe deadly Kashmir attack
-
Volkswagen unveils its electric counter-offensive in China

-
 Landmark Nepal survey estimates nearly 400 elusive snow leopards
Landmark Nepal survey estimates nearly 400 elusive snow leopards
-
Napoleon letter auction recalls French pope detention
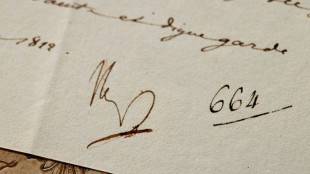
-
 Saka injury 'nothing serious' as Arteta weighs Arsenal options
Saka injury 'nothing serious' as Arteta weighs Arsenal options
-
Rubio to cut positions, rights offices at US State Department

-
 Trump says 'on the same side of every issue' with Netanyahu after call
Trump says 'on the same side of every issue' with Netanyahu after call
-
ECB's Lagarde hopes Trump won't fire US Fed chief Powell

-
 Gold hits record as Trump fuels Fed fears, Wall Street rebounds
Gold hits record as Trump fuels Fed fears, Wall Street rebounds
-
The world leaders set to attend Francis's funeral

-
 East Timor mourns Pope Francis months after emotional visit
East Timor mourns Pope Francis months after emotional visit
-
US envoy to visit Moscow as US pushes for ceasefire

-
 At least 24 killed in Kashmir attack on tourists: Indian police source
At least 24 killed in Kashmir attack on tourists: Indian police source
-
Philippine typhoon victims remember day Pope Francis brought hope

-
 IMF slashes global growth outlook on impact of Trump tariffs
IMF slashes global growth outlook on impact of Trump tariffs
-
BASF exits Xinjiang ventures after Uyghur abuse reports

-
 Nordics, Lithuania plan joint purchase of combat vehicles
Nordics, Lithuania plan joint purchase of combat vehicles
-
Gold hits record, stocks diverge as Trump fuels Fed fears


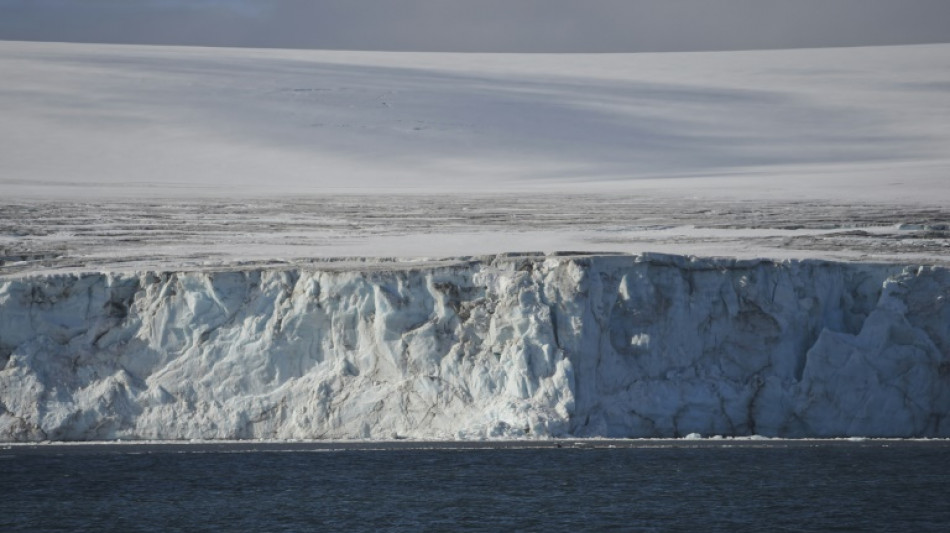
Runaway W. Antarctic ice sheet collapse not 'inevitable': study
The runaway collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet -- which would trigger catastrophic sea level rise -- is not "inevitable", scientists said Monday following research that tracked the region's recent response to climate change.
As global temperatures rise, there is mounting concern that warming could trigger so-called tipping points that set off irreversible melting of the world's massive ice sheets and ultimately lift oceans enough to drastically redraw the world map.
New research published Monday suggests a complex interaction of factors affecting the melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is home to the enormous and unstable Pine Island and Thwaites glaciers -- nicknamed the "Doomsday glacier" -- that together could raise global sea levels by more than three metres (10 feet).
Using satellite imagery as well as ocean and climate records between 2003 and 2015, an international team of researchers found that while the West Antarctic Ice Sheet continued to retreat, the pace of ice loss slowed across a vulnerable region of the coastline.
Their study, published in the journal Nature Communications, concluded that this slowdown was caused by changes in ocean temperatures that were caused by offshore winds, with pronounced differences in the impact depending on the region.
Researchers said that this raises questions about how rising temperatures will affect the Antarctic, with ocean and atmospheric conditions playing a key role.
"That means that ice-sheet collapse is not inevitable," said co-author Professor Eric Steig from the University of Washington in Seattle.
"It depends on how climate changes over the next few decades, which we could influence in a positive way by reducing greenhouse gas emissions."
The researchers observed that while in one region, in the Bellingshausen Sea, the pace of ice retreat accelerated after 2003, it slowed in the Amundsen Sea.
- 'Blink of an eye' -
They concluded that this was down to changes in the strength and direction of offshore surface winds, which can change the ocean currents and disturb the layer of cold water around Antarctica and flush relatively warmer water towards the ice.
Both the North and South pole regions have warmed by roughly three degrees Celsius compared to late 19th-century levels, nearly three times the global average.
Scientists are increasingly concerned that the Pine Island and Thwaites glaciers have reached a "tipping point" that could see irreversible melting irrespective of cuts to greenhouse gas emissions.
Anders Levermann, a climate scientist at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research who was not connected to the latest study, welcomed the approach of bringing together multiple observations and records, although the study period was "the blink of an eye in ice terms".
"I think we still have to live and plan and do our sea level projections and coastal planning with a hypothesis that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is destabilised and we will get three and a half meters of sea level rise just from this area of the planet alone," he said, adding however that this would happen "over centuries to millennia".
The United Nation's science advisory panel for climate change, the IPCC, has forecast that oceans will rise up to a metre by the end of the century, and even more after that.
Hundreds of millions of people live within a few metres of sea level.
While cutting planet-warming emissions is seen as the first and most important way to halt the melting of the West Antarctic ice sheet, scientists have also come up with an array of hi-tech suggestions for saving the gargantuan ice shelf and staving off.
Levermann has researched ideas including using snow cannons to pump trillions of tons of ice back on top of the frozen region.
Other suggestions have included constructing Eiffel Tower-sized columns on the seabed to prop it up from below, and a 100m-tall, 100-kilometre-long berm to block warm water flowing underneath.
D.Schneider--BTB




