
-
 Former England star Flintoff reveals mental battle after car crash
Former England star Flintoff reveals mental battle after car crash
-
Defending champion Korda chases first win of season at Chevron Championship

-
 Olmo fires Liga leaders Barca past Mallorca
Olmo fires Liga leaders Barca past Mallorca
-
Nunes strikes at the death as Man City sink Villa to boost top-five bid

-
 Tesla says profits plunge 71%, warns of 'changing political sentiment'
Tesla says profits plunge 71%, warns of 'changing political sentiment'
-
WHO announces 'significant' layoffs amid US funding cuts

-
 PSG draw with Nantes to stay unbeaten in Ligue 1
PSG draw with Nantes to stay unbeaten in Ligue 1
-
Trump's administration moves to ban artificial food dyes

-
 Gunmen kill dozens of civilians in Kashmir tourist hotspot
Gunmen kill dozens of civilians in Kashmir tourist hotspot
-
US Treasury chief expects China tariff impasse to de-escalate

-
 I.Coast opposition leader Thiam barred from presidential election
I.Coast opposition leader Thiam barred from presidential election
-
Top US court leans toward parents in case on LGBTQ books in schools

-
 At least 24 killed in Kashmir attack on tourists
At least 24 killed in Kashmir attack on tourists
-
Rahul powers Delhi to big win over Lucknow in IPL

-
 Colombian cycling star 'Lucho' Herrera denies murder conspiracy
Colombian cycling star 'Lucho' Herrera denies murder conspiracy
-
Trump, Zelensky to attend Pope Francis's funeral Saturday

-
 US State Department to cut positions, rights offices
US State Department to cut positions, rights offices
-
Ukraine ready for direct talks with Russia only after ceasefire: Zelensky

-
 Myanmar Catholics mourn pope who remembered their plight
Myanmar Catholics mourn pope who remembered their plight
-
Pope's Vatican 'family' pay tearful respects

-
 The world leaders set to attend Pope Francis's funeral
The world leaders set to attend Pope Francis's funeral
-
'Like a storm': Witnesses describe deadly Kashmir attack

-
 Volkswagen unveils its electric counter-offensive in China
Volkswagen unveils its electric counter-offensive in China
-
Landmark Nepal survey estimates nearly 400 elusive snow leopards

-
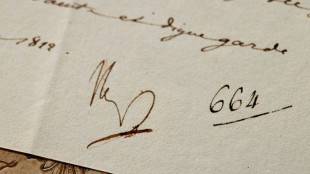 Napoleon letter auction recalls French pope detention
Napoleon letter auction recalls French pope detention
-
Saka injury 'nothing serious' as Arteta weighs Arsenal options

-
 Rubio to cut positions, rights offices at US State Department
Rubio to cut positions, rights offices at US State Department
-
Trump says 'on the same side of every issue' with Netanyahu after call

-
 ECB's Lagarde hopes Trump won't fire US Fed chief Powell
ECB's Lagarde hopes Trump won't fire US Fed chief Powell
-
Gold hits record as Trump fuels Fed fears, Wall Street rebounds

-
 The world leaders set to attend Francis's funeral
The world leaders set to attend Francis's funeral
-
East Timor mourns Pope Francis months after emotional visit

-
 US envoy to visit Moscow as US pushes for ceasefire
US envoy to visit Moscow as US pushes for ceasefire
-
At least 24 killed in Kashmir attack on tourists: Indian police source

-
 Philippine typhoon victims remember day Pope Francis brought hope
Philippine typhoon victims remember day Pope Francis brought hope
-
IMF slashes global growth outlook on impact of Trump tariffs

-
 BASF exits Xinjiang ventures after Uyghur abuse reports
BASF exits Xinjiang ventures after Uyghur abuse reports
-
Nordics, Lithuania plan joint purchase of combat vehicles

-
 Gold hits record, stocks diverge as Trump fuels Fed fears
Gold hits record, stocks diverge as Trump fuels Fed fears
-
World could boost growth by reducing trade doubt: IMF chief economist

-
 IMF slashes global growth outlook on impact of US tariffs
IMF slashes global growth outlook on impact of US tariffs
-
IMF slashes China growth forecasts as trade war deepens

-
 Skipper Shanto leads Bangladesh fightback in Zimbabwe Test
Skipper Shanto leads Bangladesh fightback in Zimbabwe Test
-
US VP Vance says 'progress' in India trade talks

-
 Ex-England star Youngs to retire from rugby
Ex-England star Youngs to retire from rugby
-
Black Ferns star Woodman-Wickliffe returning for World Cup

-
 Kremlin warns against rushing Ukraine talks
Kremlin warns against rushing Ukraine talks
-
Mbappe aiming for Copa del Rey final return: Ancelotti

-
 US universities issue letter condemning Trump's 'political interference'
US universities issue letter condemning Trump's 'political interference'
-
Pope Francis's unfulfilled wish: declaring PNG's first saint


Study explains surprise surge in methane during pandemic lockdown
A mysterious surge in planet-heating atmospheric methane in 2020 despite Covid lockdowns that reduced many human-caused sources can be explained by a greater release from nature and, surprisingly, reduced air pollution, scientists said Wednesday.
Methane stays in the atmosphere only a fraction as long as carbon dioxide, but is far more efficient at trapping heat and is responsible for roughly 30 percent of the global rise in temperatures to date.
Released from the oil and gas, waste and agriculture sectors, as well as through biological processes in wetlands, the powerful greenhouse gas is a key target for efforts to curb global warming.
But a new study published in the journal Nature suggests that cutting methane may be even more of a challenge -- and more urgent -- than is currently understood.
Researchers in China, France, the US and Norway found that efforts to reduce CO2 emissions and air pollution will affect the atmospheric process that scrubs methane from the air. That means the planet-heating gas will linger longer and accumulate faster.
If the world is to meet the challenge of keeping warming to under 2 degrees Celsius since the pre-industrial era, "we will have to act even more quickly and even more strongly to reduce methane", said Philippe Ciais who co-led the research at France's Laboratory for the Sciences of Climate and Environment (LSCE).
The researchers focused on the mystery of the concentrations of methane in the atmosphere in 2020, which had their biggest increase on record even as Covid-19 lockdowns saw carbon dioxide emissions fall.
- 'Bad news' -
What they found is potentially two pieces of "bad news" for climate change, said co-author Marielle Saunois of (LSCE).
Firstly, they looked at inventories to assess fossil fuel and agricultural methane emissions and found that human sources of methane did indeed fall slightly in 2020.
Then they used ecosystem models to estimate that warmer and wetter conditions over parts of the northern hemisphere caused a surge in emissions from wetlands.
That confirms other research and is worrying because the more methane released, the more warming, potentially creating a feedback loop largely outside of human control.
But that is only half of the story, the researchers found.
Researchers also looked at changes in atmospheric chemistry, because this provides a "sink" for methane, effectively cleaning it out of the air in a relatively short period by converting it to water and CO2 when it reacts with the hydroxyl radical (OH).
These hydroxyl radicals are present in tiny quantities and have a lifetime of less than a second, but they remove about 85 percent of methane from the atmosphere.
They are the "Pac-Man of the atmosphere", said Ciais: "As soon as they see something they eat it and then disappear."
- 'Dramatic' -
The researchers simulated changes in OH using human sources of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxide emissions that altogether affect the production and loss of hydroxyl radicals in the atmosphere.
They found that OH concentrations decreased by around 1.6 percent in 2020 from the year before, largely because of a fall in nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions caused by the Covid lockdowns. Nitrogen oxide is emitted into the air primarily from burning fuel.
A 20 percent reduction in NOx could increase methane twice as fast, Cias told a press briefing, adding: "This has surprised us greatly."
The researchers said their study helps to solve the riddle of the rise in methane in the atmosphere in 2020.
But they acknowledged that more work would have to be done to answer the next mystery: why the rise in methane concentrations hit a new record in 2021.
Ciais said lower nitrogen oxide emissions from transport in the United States and India, as well as continued low levels of air travel due to the pandemic may have played a part.
Euan Nisbet, a professor of Earth Sciences at Royal Holloway University who was not involved in the research, said the jump in methane in 2020 was a "major shock".
"Even more worrying is the rise in methane in 2021 -- this was after the major Coronavirus shutdowns when the economy was recovering," he told AFP.
"As yet we don't have detailed studies but something very dramatic seems to be going on."
E.Schubert--BTB




