
-
 Arsenal oust holders Real Madrid to reach Champions League semis
Arsenal oust holders Real Madrid to reach Champions League semis
-
Arsenal defeat Real Madrid to reach Champions League semis

-
 AMD says US rule on chips to China could cost it $800 mn
AMD says US rule on chips to China could cost it $800 mn
-
Inter hold off Bayern to reach Champions League last four

-
 El Salvador rejects US senator's plea to free wrongly deported migrant
El Salvador rejects US senator's plea to free wrongly deported migrant
-
Newcastle thrash Crystal Palace to go third in Premier League

-
 Zuckerberg denies Meta bought rivals to conquer them
Zuckerberg denies Meta bought rivals to conquer them
-
Starc stars as Delhi beat Rajasthan in Super Over

-
 Weinstein asks to sleep in hospital, citing prison 'mistreatment'
Weinstein asks to sleep in hospital, citing prison 'mistreatment'
-
Amorim asks McIlroy to bring Masters magic to Man Utd

-
 Ruud keeps Barcelona Open defence on course
Ruud keeps Barcelona Open defence on course
-
Trump tariffs could put US Fed in a bind, Powell warns

-
 CONCACAF chief rejects 64-team World Cup plan for 2030
CONCACAF chief rejects 64-team World Cup plan for 2030
-
Putin praises Musk, compares him to Soviet space hero

-
 Son to miss Spurs' Europa League trip to Frankfurt
Son to miss Spurs' Europa League trip to Frankfurt
-
US senator in El Salvador seeking release of wrongly deported migrant

-
 Trump tariffs could put the US Fed in a bind, Powell warns
Trump tariffs could put the US Fed in a bind, Powell warns
-
US judge says 'probable cause' to hold Trump admin in contempt

-
 India opposition slams graft charges against Gandhis
India opposition slams graft charges against Gandhis
-
Nate Bargatze to host Emmys: organizers

-
 US Fed Chair warns of 'tension' between employment, inflation goals
US Fed Chair warns of 'tension' between employment, inflation goals
-
Trump touts trade talks, China calls out tariff 'blackmail'

-
 US judge says 'probable cause' to hold govt in contempt over deportations
US judge says 'probable cause' to hold govt in contempt over deportations
-
US eliminates unit countering foreign disinformation

-
 Germany sees 'worrying' record dry spell in early 2025
Germany sees 'worrying' record dry spell in early 2025
-
Israel says 30 percent of Gaza turned into buffer zone

-
 TikTok tests letting users add informative 'Footnotes'
TikTok tests letting users add informative 'Footnotes'
-
Global uncertainty will 'certainly' hit growth: World Bank president

-
 EU lists seven 'safe' countries of origin, tightening asylum rules
EU lists seven 'safe' countries of origin, tightening asylum rules
-
Chelsea fans must 'trust' the process despite blip, says Maresca

-
 Rebel rival government in Sudan 'not the answer': UK
Rebel rival government in Sudan 'not the answer': UK
-
Prague zoo breeds near-extinct Brazilian mergansers

-
 Macron to meet Rubio, Witkoff amid transatlantic tensions
Macron to meet Rubio, Witkoff amid transatlantic tensions
-
WTO chief says 'very concerned' as tariffs cut into global trade

-
 Sports bodies have 'no excuses' on trans rules after court ruling: campaigners
Sports bodies have 'no excuses' on trans rules after court ruling: campaigners
-
Zverev joins Shelton in Munich ATP quarters

-
 The Trump adviser who wants to rewrite the global financial system
The Trump adviser who wants to rewrite the global financial system
-
US senator travels to El Salvador over wrongly deported migrant

-
 UN watchdog chief says Iran 'not far' from nuclear bomb
UN watchdog chief says Iran 'not far' from nuclear bomb
-
Trump says 'joke' Harvard should be stripped of funds

-
 Macron vows punishment for French prison attackers
Macron vows punishment for French prison attackers
-
Canada central bank holds interest rate steady amid tariffs chaos

-
 Rubio headed to Paris for Ukraine war talks
Rubio headed to Paris for Ukraine war talks
-
Australian PM vows not to bow to Trump on national interest

-
 New attacks target France prison guard cars, home
New attacks target France prison guard cars, home
-
Global trade uncertainty could have 'severe negative consequences': WTO chief

-
 Google facing £5 bn UK lawsuit over ad searches: firms
Google facing £5 bn UK lawsuit over ad searches: firms
-
Onana to return in goal for Man Utd against Lyon: Amorim

-
 Tiktok bans user behind Gisele Pelicot 'starter kit' meme
Tiktok bans user behind Gisele Pelicot 'starter kit' meme
-
'Put it on': Dutch drive for bike helmets


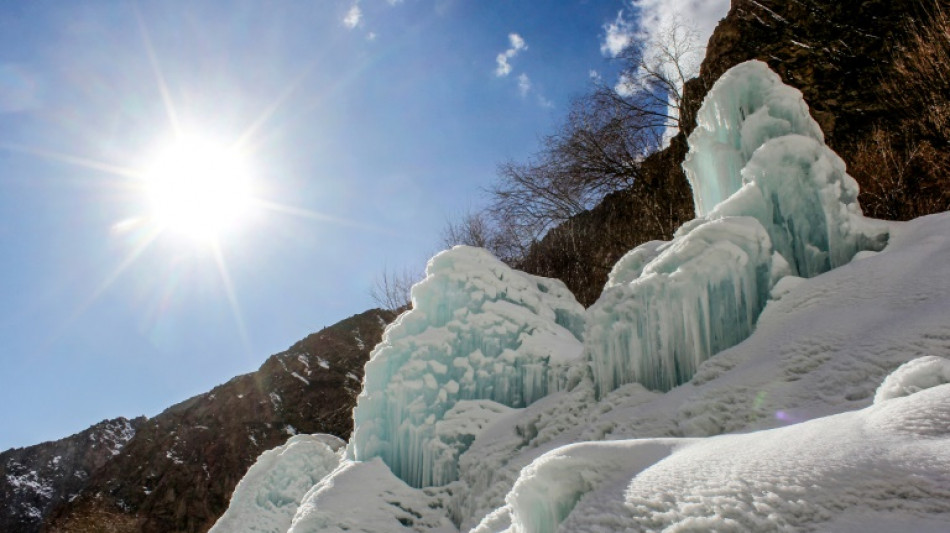
Artificial glaciers boost water supply in northern Pakistan
At the foot of Pakistan's impossibly high mountains whitened by frost all year round, farmers grappling with a lack of water have created their own ice towers.
Warmer winters as a result of climate change has reduced the snow fall and subsequent seasonal snowmelt that feeds the valleys of Gilgit-Baltistan, a remote region home to K2, the world's second-highest peak.
Farmers in the Skardu valley, at an altitude of up to 2,600 metres (8,200 feet) in the shadow of the Karakoram mountain range, searched online for help in how to irrigate their apple and apricot orchards.
"We discovered artificial glaciers on YouTube," Ghulam Haider Hashmi told AFP.
They watched the videos of Sonam Wangchuk, an environmental activist and engineer in the Indian region of Ladakh, less than 200 kilometres away across a heavily patrolled border, who developed the technique about 10 years ago.
Water is piped from streams into the village, and sprayed into the air during the freezing winter temperatures.
"The water must be propelled so that it freezes in the air when temperatures drop below zero, creating ice towers," said Zakir Hussain Zakir, a professor at the University of Baltistan.
The ice forms in the shape of cones that resemble Buddhist stupas, and act as a storage system -- steadily melting throughout spring when temperatures rise.
- 'Ice stupas' -
Gilgit-Baltistan has 13,000 glaciers -- more than any other country on Earth outside the polar regions.
Their beauty has made the region one of the country's top tourist destinations -- towering peaks loom over the Old Silk Road, still visible from a highway transporting tourists between cherry orchards, glaciers and ice-blue lakes.
Sher Muhammad, a specialist in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan mountain range that stretches from Afghanistan to Myanmar, however said most of the region's water supply comes from snow melt in spring, with a fraction from annual glacial melt in summers.
"From late October until early April, we were receiving heavy snowfall. But in the past few years, it's quite dry," Muhammad, a researcher at the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD), told AFP.
The first "ice stupas" in Gilgit-Baltistan were created in 2018.
Now, more than 20 villages make them every winter, and "more than 16,000 residents have access to water without having to build reservoirs or tanks", said Rashid-ud-Din, provincial head of GLOF-2, a UN-Pakistan plan to adapt to the effects of climate change.
Farmer Muhammad Raza told AFP that eight stupas were built in his village of Hussainabad this winter, trapping approximately 20 million litres of water in the ice.
"We no longer have water shortages during planting," he said, since the open-air reservoirs appeared on the slopes of the valley.
"Before, we had to wait for the glaciers to melt in June to get water, but the stupas saved our fields," said Ali Kazim, also a farmer in the valley.
- Harvest seasons multiply -
Before the stupas, "we planted our crops in May", said 26-year-old Bashir Ahmed who grows potatoes, wheat and barley in nearby Pari village which has also adopted the method.
And "we only had one growing season, whereas now we can plant two or three times" a year.
Temperatures in Pakistan rose twice as fast between 1981 and 2005 compared to the global average, putting the country on the front line of climate change impacts, including water scarcity.
Its 240 million inhabitants live in a territory that is 80 percent arid or semi-arid and depends on rivers and streams originating in neighbouring countries for more than three-quarters of its water.
Glaciers are melting rapidly in Pakistan and across the world, with a few exceptions including the Karakoram mountain range, increasing the risk of flooding and reducing water supply over the long term.
"Faced with climate change, there are neither rich nor poor, neither urban nor rural; the whole world has become vulnerable," said 24-year-old Yasir Parvi.
"In our village, with the ice stupas, we decided to take a chance."
H.Kuenzler--VB


