-
 Zuckerberg denies Meta bought rivals to conquer them
Zuckerberg denies Meta bought rivals to conquer them
-
Starc stars as Delhi beat Rajasthan in Super Over

-
 Weinstein asks to sleep in hospital, citing prison 'mistreatment'
Weinstein asks to sleep in hospital, citing prison 'mistreatment'
-
Amorim asks McIlroy to bring Masters magic to Man Utd

-
 Ruud keeps Barcelona Open defence on course
Ruud keeps Barcelona Open defence on course
-
Trump tariffs could put US Fed in a bind, Powell warns

-
 CONCACAF chief rejects 64-team World Cup plan for 2030
CONCACAF chief rejects 64-team World Cup plan for 2030
-
Putin praises Musk, compares him to Soviet space hero

-
 Son to miss Spurs' Europa League trip to Frankfurt
Son to miss Spurs' Europa League trip to Frankfurt
-
US senator in El Salvador seeking release of wrongly deported migrant

-
 Trump tariffs could put the US Fed in a bind, Powell warns
Trump tariffs could put the US Fed in a bind, Powell warns
-
US judge says 'probable cause' to hold Trump admin in contempt

-
 India opposition slams graft charges against Gandhis
India opposition slams graft charges against Gandhis
-
Nate Bargatze to host Emmys: organizers

-
 US Fed Chair warns of 'tension' between employment, inflation goals
US Fed Chair warns of 'tension' between employment, inflation goals
-
Trump touts trade talks, China calls out tariff 'blackmail'

-
 US judge says 'probable cause' to hold govt in contempt over deportations
US judge says 'probable cause' to hold govt in contempt over deportations
-
US eliminates unit countering foreign disinformation

-
 Germany sees 'worrying' record dry spell in early 2025
Germany sees 'worrying' record dry spell in early 2025
-
Israel says 30 percent of Gaza turned into buffer zone

-
 TikTok tests letting users add informative 'Footnotes'
TikTok tests letting users add informative 'Footnotes'
-
Global uncertainty will 'certainly' hit growth: World Bank president

-
 EU lists seven 'safe' countries of origin, tightening asylum rules
EU lists seven 'safe' countries of origin, tightening asylum rules
-
Chelsea fans must 'trust' the process despite blip, says Maresca

-
 Rebel rival government in Sudan 'not the answer': UK
Rebel rival government in Sudan 'not the answer': UK
-
Prague zoo breeds near-extinct Brazilian mergansers

-
 Macron to meet Rubio, Witkoff amid transatlantic tensions
Macron to meet Rubio, Witkoff amid transatlantic tensions
-
WTO chief says 'very concerned' as tariffs cut into global trade

-
 Sports bodies have 'no excuses' on trans rules after court ruling: campaigners
Sports bodies have 'no excuses' on trans rules after court ruling: campaigners
-
Zverev joins Shelton in Munich ATP quarters

-
 The Trump adviser who wants to rewrite the global financial system
The Trump adviser who wants to rewrite the global financial system
-
US senator travels to El Salvador over wrongly deported migrant

-
 UN watchdog chief says Iran 'not far' from nuclear bomb
UN watchdog chief says Iran 'not far' from nuclear bomb
-
Trump says 'joke' Harvard should be stripped of funds

-
 Macron vows punishment for French prison attackers
Macron vows punishment for French prison attackers
-
Canada central bank holds interest rate steady amid tariffs chaos

-
 Rubio headed to Paris for Ukraine war talks
Rubio headed to Paris for Ukraine war talks
-
Australian PM vows not to bow to Trump on national interest

-
 New attacks target France prison guard cars, home
New attacks target France prison guard cars, home
-
Global trade uncertainty could have 'severe negative consequences': WTO chief

-
 Google facing £5 bn UK lawsuit over ad searches: firms
Google facing £5 bn UK lawsuit over ad searches: firms
-
Onana to return in goal for Man Utd against Lyon: Amorim

-
 Tiktok bans user behind Gisele Pelicot 'starter kit' meme
Tiktok bans user behind Gisele Pelicot 'starter kit' meme
-
'Put it on': Dutch drive for bike helmets

-
 China's Xi meets Malaysian leaders, vows to 'safeguard' Asia allies
China's Xi meets Malaysian leaders, vows to 'safeguard' Asia allies
-
France urges release of jailed Russian journalists who covered Navalny

-
 Gabon striker Boupendza dies after 11th floor fall
Gabon striker Boupendza dies after 11th floor fall
-
UK top court rules definition of 'woman' based on sex at birth

-
 PSG keep Champions League bid alive, despite old ghosts reappearing
PSG keep Champions League bid alive, despite old ghosts reappearing
-
Stocks retreat as US hits Nvidia chip export to China


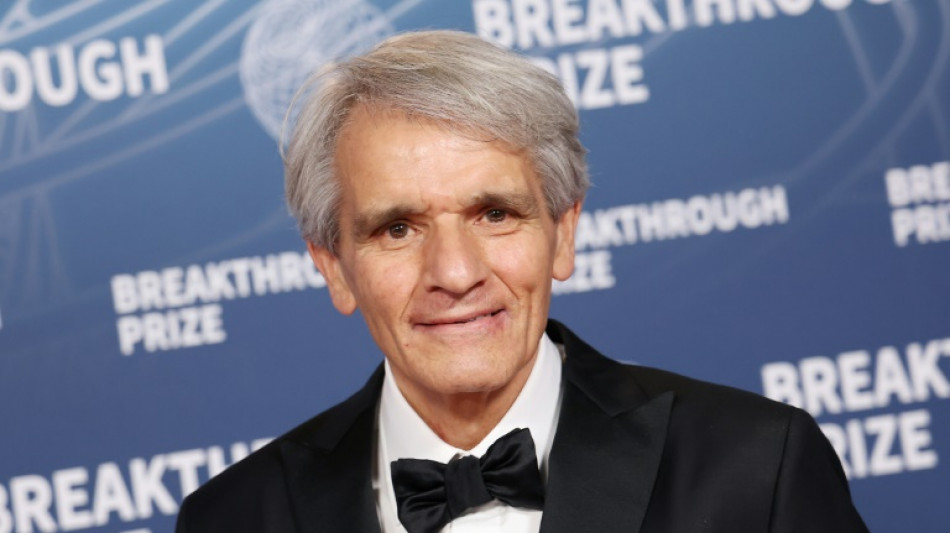
Research on multiple sclerosis wins 'Oscars of science'
An American neurologist and an Italian epidemiologist whose work revolutionized the treatment of multiple sclerosis on Saturday won a prestigious Breakthrough Prize, the award nicknamed the "Oscars of science."
Stephen Hauser and Alberto Ascherio were recognized for their decades researching the debilitating neurodegenerative disease, which affects nearly three million people worldwide and was long considered an impenetrable enigma.
Hauser's work on multiple sclerosis (MS) started more than 45 years ago, when he met a young patient named Andrea, "an extraordinarily talented young woman who was already an attorney" and working at the White House under then-president Jimmy Carter, he told AFP.
"Then MS appeared in an explosive fashion and destroyed her life," he said.
"I remember seeing her, unable to speak, paralyzed on the right side, unable to swallow, and soon, unable to breathe on her own, and I remember thinking that this was the most unfair thing I had ever seen in medicine."
Then 27 years old, he decided to make it his life's work.
- Rough road -
"At the time, we had no treatments for MS. In fact, there was also a pessimism that treatments could ever be developed," said Hauser, now 74 and director of the neuroscience institute at the University of California San Francisco.
Scientists knew the disease, which damages the central nervous system and leads to paralyzing cognitive and motor problems, was caused by the immune system turning on the body.
But they thought the white blood cells known as T cells were the lone culprit.
Hauser questioned that.
Studying the role played in the disease by B cells, another type of white blood cell, he and his colleagues managed to recreate the damage MS causes to the human nervous system in small monkeys known as marmosets.
The US federal body overseeing medical research dismissed the link as "biologically implausible," and turned down their application for funding for a clinical trial.
But Hauser and his team pressed on.
They persuaded pharmaceutical company Genentech to back testing. In 2006, they got resounding results: treatments targeting B cells were associated with "a dramatic, more than 90-percent reduction in brain inflammation," Hauser said.
It was "something of a scope that had never been seen before."
That threw open a door to bring new treatments to market that slow the advance of the disease in many patients.
But it also raised other questions. For example, what would cause our white blood cells to turn against us?
- The virus connection -
That was a question that puzzled Ascherio, today a professor at Harvard.
He decided to investigate why MS mostly affected people in the northern hemisphere.
"The geographical distribution of MS was quite striking," he told AFP.
"MS is very uncommon in tropical countries and near the equator."
That made him wonder whether a virus could be involved.
He and his team carried out a long-term study following millions of young US military recruits.
After nearly 20 years of research, they came up with an answer. In 2022, they confirmed a link between MS and the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a common infection responsible for another well-known disease, infectious mononucleosis, or mono.
"Most people infected with EBV will never develop MS," said Ascherio, 72.
But everyone who develops MS has had EBV first.
The discovery still did not explain why MS occurs. But it fuelled hope of finding new treatments and preventive measures for a disease that remains uncurable, and whose current treatments do not work on all patients.
Ascherio's breakthrough could also help treat other conditions.
"We are now trying also to extend our investigation, to investigate the role of viral infection in other neurodegenerative diseases, like Alzheimer's or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis," also known as ALS or Lou Gehrig's disease, he said.
The link remains theoretical for now. But "there is some evidence," he said.
"It's like where we were on MS 20 or 30 years ago."
L.Maurer--VB