
-
 Rugby Australia hits out at French clubs poaching young talent
Rugby Australia hits out at French clubs poaching young talent
-
Canada PM Carney avoids French blunder as he faces attack in key debate

-
 El Salvador becoming 'black hole' for US deportees, critics fear
El Salvador becoming 'black hole' for US deportees, critics fear
-
Trump admin proposes redefining 'harm' to endangered animals

-
 Australia's Mary Fowler set for long lay-off after ACL injury
Australia's Mary Fowler set for long lay-off after ACL injury
-
Rubio to meet French leaders for talks on Ukraine

-
 Webb spots strongest 'hints' yet of life on distant planet
Webb spots strongest 'hints' yet of life on distant planet
-
Arteta's Arsenal come of age with Madrid masterclass

-
 None spared in Nigeria gun, machete massacre: survivors
None spared in Nigeria gun, machete massacre: survivors
-
'No problem' if Real Madrid replace me: Ancelotti

-
 Inter dreaming of treble glory after reaching Champions League semis
Inter dreaming of treble glory after reaching Champions League semis
-
'No limits' for treble-hunting Inter, says Pavard

-
 Inter off Bayern to reach Champions League last four
Inter off Bayern to reach Champions League last four
-
Rice 'knew' Arsenal would dethrone Real Madrid

-
 US stocks fall with dollar as Powell warns on tariffs
US stocks fall with dollar as Powell warns on tariffs
-
Arsenal oust holders Real Madrid to reach Champions League semis

-
 Arsenal defeat Real Madrid to reach Champions League semis
Arsenal defeat Real Madrid to reach Champions League semis
-
AMD says US rule on chips to China could cost it $800 mn
-
 Inter hold off Bayern to reach Champions League last four
Inter hold off Bayern to reach Champions League last four
-
El Salvador rejects US senator's plea to free wrongly deported migrant

-
 Newcastle thrash Crystal Palace to go third in Premier League
Newcastle thrash Crystal Palace to go third in Premier League
-
Zuckerberg denies Meta bought rivals to conquer them

-
 Starc stars as Delhi beat Rajasthan in Super Over
Starc stars as Delhi beat Rajasthan in Super Over
-
Weinstein asks to sleep in hospital, citing prison 'mistreatment'

-
 Amorim asks McIlroy to bring Masters magic to Man Utd
Amorim asks McIlroy to bring Masters magic to Man Utd
-
Ruud keeps Barcelona Open defence on course

-
 Trump tariffs could put US Fed in a bind, Powell warns
Trump tariffs could put US Fed in a bind, Powell warns
-
CONCACAF chief rejects 64-team World Cup plan for 2030

-
 Putin praises Musk, compares him to Soviet space hero
Putin praises Musk, compares him to Soviet space hero
-
Son to miss Spurs' Europa League trip to Frankfurt

-
 US senator in El Salvador seeking release of wrongly deported migrant
US senator in El Salvador seeking release of wrongly deported migrant
-
Trump tariffs could put the US Fed in a bind, Powell warns

-
 US judge says 'probable cause' to hold Trump admin in contempt
US judge says 'probable cause' to hold Trump admin in contempt
-
India opposition slams graft charges against Gandhis

-
 Nate Bargatze to host Emmys: organizers
Nate Bargatze to host Emmys: organizers
-
US Fed Chair warns of 'tension' between employment, inflation goals

-
 Trump touts trade talks, China calls out tariff 'blackmail'
Trump touts trade talks, China calls out tariff 'blackmail'
-
US judge says 'probable cause' to hold govt in contempt over deportations

-
 US eliminates unit countering foreign disinformation
US eliminates unit countering foreign disinformation
-
Germany sees 'worrying' record dry spell in early 2025

-
 Israel says 30 percent of Gaza turned into buffer zone
Israel says 30 percent of Gaza turned into buffer zone
-
TikTok tests letting users add informative 'Footnotes'

-
 Global uncertainty will 'certainly' hit growth: World Bank president
Global uncertainty will 'certainly' hit growth: World Bank president
-
EU lists seven 'safe' countries of origin, tightening asylum rules

-
 Chelsea fans must 'trust' the process despite blip, says Maresca
Chelsea fans must 'trust' the process despite blip, says Maresca
-
Rebel rival government in Sudan 'not the answer': UK

-
 Prague zoo breeds near-extinct Brazilian mergansers
Prague zoo breeds near-extinct Brazilian mergansers
-
Macron to meet Rubio, Witkoff amid transatlantic tensions

-
 WTO chief says 'very concerned' as tariffs cut into global trade
WTO chief says 'very concerned' as tariffs cut into global trade
-
Sports bodies have 'no excuses' on trans rules after court ruling: campaigners


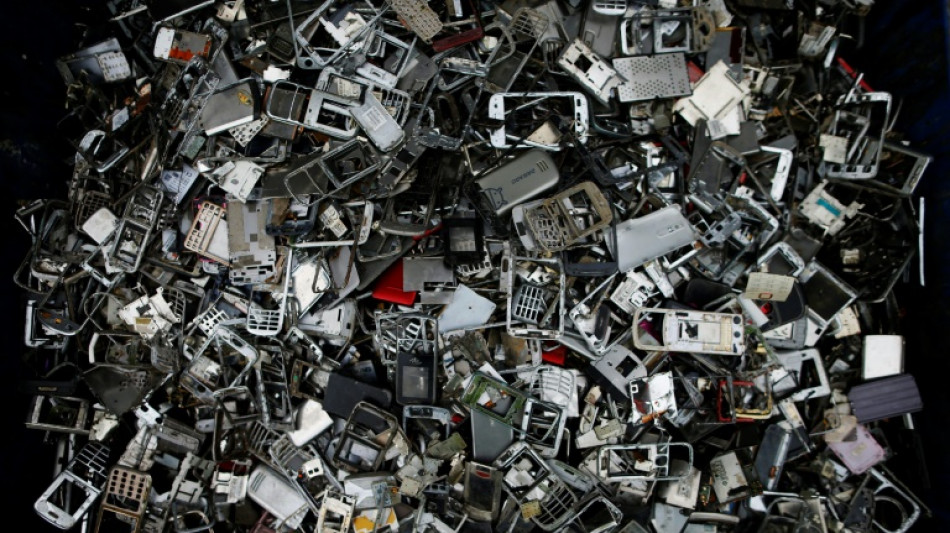
'Throwaway economy' thwarting climate goals: report
Countries are neglecting the massive impact of the "throwaway" economy on planet-warming emissions, according to research published Wednesday that calculated more than half a trillion tonnes of virgin materials have been consumed since the 2015 Paris climate deal.
From clothing to food, planes to buildings, research by the organisation Circle Economy estimates that 70 percent of greenhouse gas emissions are linked to the manufacturing and use of products.
But in its annual report on the state of the world's use of materials, researchers said national climate pledges to reduce emissions focus narrowly on fossil fuel use and ignore the mounting global appetite for stuff.
Matthew Fraser, head of research at Circle Economy, said the report aimed to look beyond just fossil fuel use and the transition to green energy and ask about the emissions implications of using fewer resources.
"What if we reimagine our relationship with stuff, what would that bring us? Actually, it is quite significant," he told AFP.
The report estimates that if the economy were more circular, reducing resource extraction and consumption by 28 percent, then the world could meet the Paris warming target of 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
But only a third of nations' climate pledges mention the circular economy as part of their emissions goals, the report said.
It warns that humanity is consuming 70 percent more virgin materials than the world can safely replenish.
- Economic 'metabolism' -
The analysis looks at global material flows based on national import and export figures and translates them into estimates of materials used -- and reused.
It calculates annual resource use has grown from 89.8 billion tonnes in 2016 to more than 100 billion tonnes in 2019 and estimated it at 101.4 billion last year.
Circle Economy found that almost all of the materials extracted go to waste, with just 8.6 percent of materials recycled in 2020, what they call the circularity gap.
That is an even lower proportion than in 2018, when reused materials were 9.1 percent of the total, as the global demand for more things surges.
"Even though we are getting more efficient with how we use materials -- computers are getting smaller, cars are becoming lighter, recycling is getting better -- these micro gains in efficiency just aren't stacking up relative to the total increasing demand," said Fraser.
The report identified a number of practices across sectors from food production to transportation that it said could help rein in the ever-expanding use of virgin materials.
Fraser said the model that enables people in richer countries to buy products from all over the world to be delivered within hours and days "will inevitably have to change".
The report also weighed strategies like enabling electrical goods -- which contain critical raw materials including gold, silver and cobalt -- to be repaired, redesigning items to be easier to recycle, restricting single-use plastics and renting items like cars rather than buying them.
One sector it identified as having a significant opportunity to reduce its materials footprint was buildings and construction, where Fraser said current practices were far from sustainable.
He said government policy would be needed occasionally to reconfigure the economic incentives that make reusing resources more expensive than using new ones -- stressing that this should be seen as an integral part of efforts to curb global warming.
But Fraser said for now the issue remains a significant blind spot for governments, which he said do not pull together data of their countries' materials footprint.
He added that people in the future may ask tougher questions about whether materials can be recycled before they are even used.
"Could we become more strict about the metabolism of our economy? Just like you wouldn't eat junk food all the time," he said.
"I think in the future that could become more and more prominent."
A.Gasser--BTB
